mybatis独立的配置和mybatis-spring配置项目的最终地址在这里:https://github.com/shellj/mybatis-example
Mybatis单独的配置
根据官方的例子进行配置http://www.mybatis.org/mybatis-3/zh/getting-started.html
新建maven项目
添加依赖,目前需要的依赖包如下:<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis</artifactId>
<version>3.4.1</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>ch.qos.logback</groupId>
<artifactId>logback-classic</artifactId>
<version>1.1.7</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>5.1.39</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>4.12</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
创建Blog表
CREATE TABLE blog (
`id` bigint(19) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`author` varchar(64),
`title` varchar(128),
`content` varchar(512),
`create_date` datetime,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
) ENGINE=`InnoDB` DEFAULT CHARACTER SET utf8 COLLATE utf8_general_ci COMMENT='blog';
创建实体类,mapper与mybatis config
其中mybatis config文件里需要的一些数据库配置信息通过引入properties配置文件获取,新建一个system.properties文件。mybatis-config.xml
<configuration>
<properties resource="system.properties"/>
</configuration>
system.properties
jdbc.driver=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
jdbc.url=jdbc:mysql://10.211.55.6:3306/blog?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8
jdbc.username=root
jdbc.password=******
程序验证
上面执行完大概会有下面图片的结构,当然具体的一些结构根据实际情况会有所不同。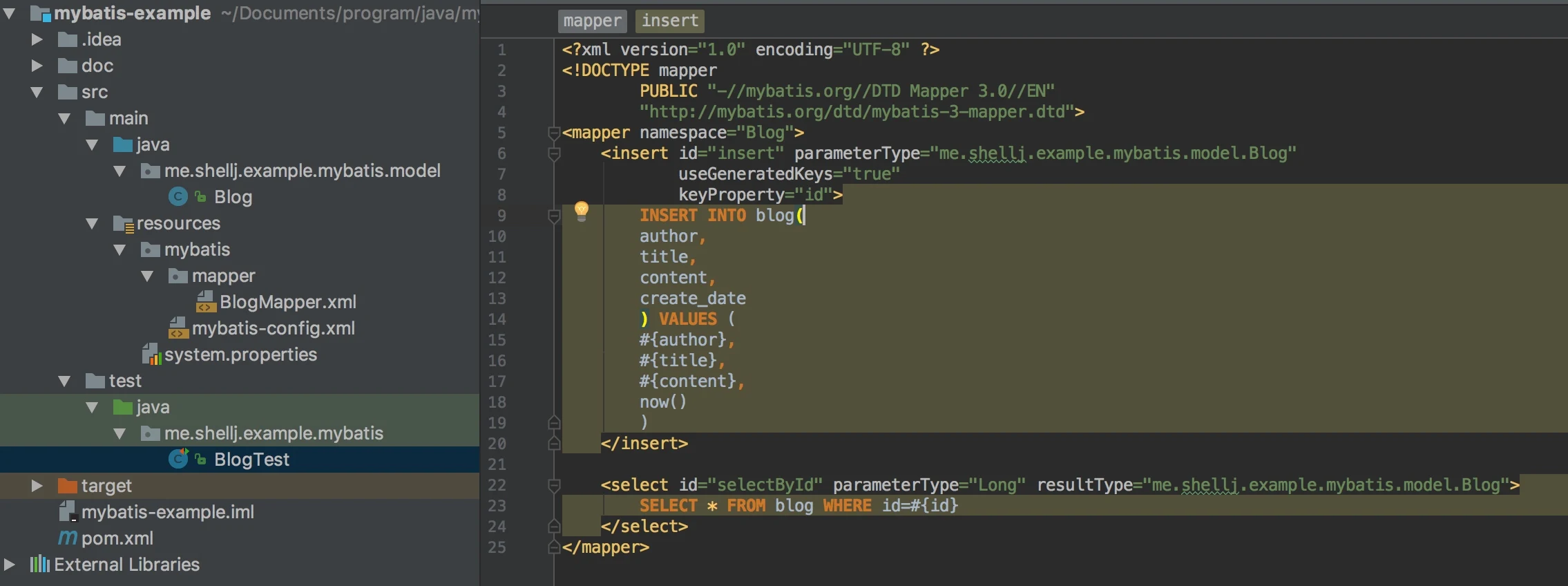 
好了,基本的mybatis数据操作就可以了,现在可以写个测试程序来测试程序是否正常运行,
public class BlogTest {
private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(BlogTest.class);
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory;
@Before
public void init() throws IOException {
String resource = "mybatis/mybatis-config.xml";
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);
sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);
}
@Test
public void insertTest() throws Exception {
Blog blog = new Blog("标题", "shellj", "很多内容");
try (SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession(true)) {
int insert = sqlSession.insert("Blog.insert", blog);
logger.info("id:" + blog.getId());
assertEquals(1, insert);
}
}
}
更好的方式
使用上面那种sqlSession.insert()方式显然有些不方便,mybatis也提供了一种更直观的操作方式,Mapper方式。添加
BlogMapper interface:public interface BlogMapper {
int insert(Blog blog);
Blog selectById(Long id);
}
BlogMapper.xml里的namespace改为me.shellj.example.mybatis.mapper.BlogMapper,至于为什么,官方有解释:你可能注意到这和使用完全限定名调用 Java 对象的方法是相似的,之所以这样做是有原因的。这个命名可以直接映射到在命名空间中同名的 Mapper 类,并在已映射的 select 语句中的名字、参数和返回类型匹配成方法。这样你就可以向上面那样很容易地调用这个对应 Mapper 接口的方法。接下来我们就可以通过更简单的方式查询数据了:
@Test
public void selectTest() throws Exception {
try (SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession(true)) {
BlogMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(BlogMapper.class);
Blog blog = mapper.selectById(1L);
assertNotNull(blog);
logger.info(blog.toString());
}
}
BlogMapper.java里面,但推荐都写在xml映射文件里。mybatis-spring
http://www.mybatis.org/spring/zh/getting-started.html主要是设置
SqlSessionFactoryBean和MapperScannerConfigurer就好了,xml,mapper和model不需要变,把下面的相应地址改掉就好了,配置如下:<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<bean class="org.springframework.beans.factory.config.PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer">
<property name="location" value="system.properties"/>
<property name="fileEncoding" value="utf-8"/>
</bean>
<bean id="dataSource" class="org.apache.commons.dbcp2.BasicDataSource" destroy-method="close">
<property name="driverClassName" value="${jdbc.driver}"/>
<property name="url" value="${jdbc.url}"/>
<property name="username" value="${jdbc.username}"/>
<property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}"/>
<property name="minEvictableIdleTimeMillis" value="7200000"/>
<property name="testWhileIdle" value="true"/>
<property name="validationQuery" value="select 'x'"/>
</bean>
<bean id="sqlSessionFactory" class="org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionFactoryBean">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/>
<property name="mapperLocations" value="spring/mapper/*.xml"/>
</bean>
<bean class="org.mybatis.spring.mapper.MapperScannerConfigurer">
<property name="sqlSessionFactoryBeanName" value="sqlSessionFactory"/>
<property name="basePackage" value="me.shellj.example.spring.mapper"/>
</bean>
<context:component-scan base-package="me.shellj.example.spring"></context:component-scan>
</beans>
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@ContextConfiguration(locations = "classpath:spring/mybatis-spring.xml")
public class SpringBlogTest {
private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(SpringBlogTest.class);
@Autowired
private BlogMapper blogMapper;
@Test
public void insert() throws Exception {
Blog blog = new Blog();
blog.setAuthor("名字spring");
blog.setTitle("title");
blog.setContent("content");
int insert = blogMapper.insert(blog);
assertEquals(1, insert);
logger.info(blog.toString());
}
@Test
public void select() throws Exception {
BlogExample example = new BlogExample();
example.createCriteria().andAuthorEqualTo("名字spring");
List<Blog> blogs = blogMapper.selectByExample(example);
assertNotNull(blogs);
assertEquals(1, blogs.size());
logger.info(blogs.get(0).toString());
}
}